Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, and suspended solids and gases from water with the goal of producing water fit for a specific purpose. Most public drinking water goes through a disinfection process, but water purification may also be designed for other purposes, including fulfilling the requirements of pharmacological, medical, chemical and industrial applications, or just to upgrade the drinking water supply. The methods used include physical processes such as sediment filtration, carbon based filtration, sedimentation with sand filters; chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination and the use of ultraviolet light or ozone. Water testing and analysis should begin the process of determining the appropriate technologies and systems to meet the goal of the end user.
For Your Home of Business
Water purification systems can be installed for the removal of almost any of the potential water quality concerns you may have. For example, lead is typically removed from drinking water with either a reverse osmosis water purification system or a carbon filter designed specifically for the removal of lead from water. Water softeners are typically installed to remove dissolved iron (see photo below) or manganese and hardness minerals in the water through a technology called Ion Exchange (see below for more information on this).

Water Softener & Sediment Filter
Water Purification – Bad Odors & Tastes
In addition to the above systems described, there are many other types of systems to remove bad tastes & odors, sediment and many other objectionable minerals and contaminants that may be present in the water. For more information on bad odors and tastes in your water, see the link at: https://bad-odor-taste-water/.

Sediment & Carbon Filtration
The Affects of Hard Water
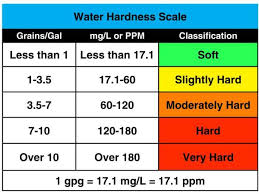
The only way to know how hard your water is by having it tested. There are on-site testing methods that are reliable or you can have a sample taken to a certified laboratory. Hard water interferes with many cleaning tasks, from doing the laundry to washing dishes to taking a shower. Washing your hair in hard water may leave it feeling sticky and dull. Dishes and glasses get spotted or streaky and a film may build up on shower doors, bathtubs, sinks and faucets. Clothing can look dingy and feel rough and scratchy. Magnesium and Calcium may also have major affects on your home’s plumbing distribution system and water using appliances, although the EPA has no published limits on these.
Scale from hard water can build-up inside water heaters insulating the temperature sensor inside the tank creating extra work to bring the temperature up to the set level. This reduces the life of your hot water heater and will likely require early replacement. Hard water can also cause scale build-up in pipes that can lower water pressure throughout the home (see photo below). Iron and manganese (“The Stainers”) can also be found in Wellesley water. Depending on whether the contaminant’s form is in solution or particulate, these contaminants can be removed with a water softener and/or a properly specified sediment water filtration installation. For more on hard water see hard water epa.

Dissolved Iron Staining
The maximum allowable level (per the Environmental Protection Agency) for iron as a secondary contaminant is .3 parts per million and for manganese is .05 parts per million. Small amounts of these minerals can have very noticeable, even damaging affects on your home’s water quality
Any water purification system recommendation should start with a water test before an informed decision can be made. To determine what type of water testing to have performed and how to take a proper sample, call a water treatment professional or a state certified laboratory.



